Understanding CT Scans for Lung Cancer: A Comprehensive Guide
Lung cancer is a pervasive and potentially fatal illness that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Early detection remains a critical component in improving survival rates and treatment outcomes. One of the most effective methods for diagnosing lung cancer is the CT scan for lung cancer. This article delves into the fundamentals of CT scans, their significance in lung cancer diagnostics, and how they are utilized in medical practice, particularly by professionals in the health and medical fields, including experts in sports medicine and physical therapy.
What is a CT Scan?
A Computed Tomography (CT) scan, often referred to simply as a CT or CAT scan, is a medical imaging technique that enables detailed visualization of the body's internal structures. Utilizing a combination of X-rays and computer technology, a CT scan creates cross-sectional images (slices) of bones, organs, and soft tissues.
How Does a CT Scan Work?
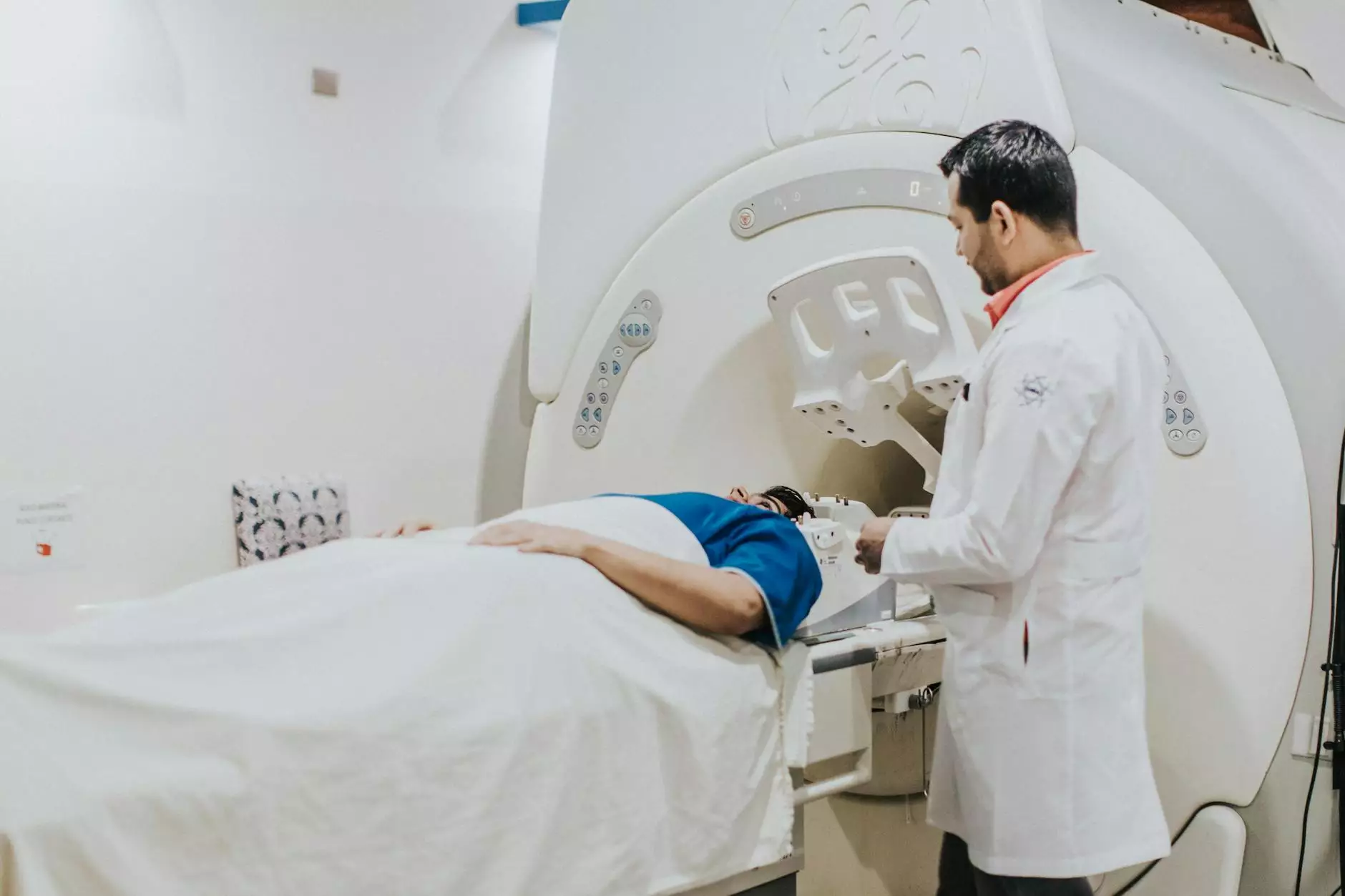
The process of conducting a CT scan involves the following steps:
- Preparation: The patient may need to refrain from eating or drinking for a certain period before the scan.
- Positioning: The patient lies on a special table that slides into the CT scanner.
- Imaging: The scanner rotates around the patient, capturing multiple images from different angles.
- Contrast Agent: In some cases, a contrast dye may be administered to enhance the visibility of structures.
The Role of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
CT scans play a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of lung cancer for several reasons:
- Early Detection: They can identify lung nodules or masses before they become symptomatic.
- Staging the Cancer: CT scans help determine the size and spread of cancerous tumors, which is essential for treatment planning.
- Monitoring Treatment Response: Regular CT scans can assess how well treatment is working by comparing changes in tumor size.
Benefits of CT Scans for Lung Cancer
The use of CT scans offers several advantages in the assessment of lung cancer:
- Non-Invasive: CT scans are generally non-invasive and painless, making them safer alternatives to more invasive diagnostic methods.
- High Sensitivity: They have a high sensitivity rate for detecting lung abnormalities compared to other imaging methods.
- Comprehensive Information: CT scans provide detailed images that assist in evaluating the lungs and surrounding structures effectively.
Interpreting CT Scan Results for Lung Cancer
Once a CT scan is completed, radiologists analyze the images to identify any potential signs of lung cancer. These signs may include:
- Lung Nodules: Small growths that may be benign or malignant.
- Masses: Larger irregularities that could indicate the presence of cancer.
- Mediastinal Adenopathy: Swollen lymph nodes that could suggest cancer spread.
Follow-Up Procedures
If suspicious findings are detected, further diagnostic procedures may be recommended, such as:
- Biopsy: A procedure to extract a small sample of tissue for laboratory analysis.
- PET Scans: Positron Emission Tomography scans can provide additional information about tumor activity.
- Bronchoscopy: A minor surgical procedure that allows doctors to examine the airways directly.
Risk Factors and Considerations for Lung Cancer
While anyone can develop lung cancer, several risk factors may increase the likelihood:
- Tobacco Use: Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer.
- Exposure to Radon: Elevated radon levels in homes can contribute to lung cancer risk.
- Occupational Hazards: Exposure to carcinogenic substances in the workplace.
- Family History: A genetic predisposition to lung cancer can increase risk.
Preparing for a CT Scan
Preparation for a CT scan can vary, but the general guidelines include:
- Informing the Doctor: Disclose any allergies, especially to contrast materials.
- Clothing: Wear comfortable clothing; you may be asked to change into a hospital gown.
- Follow Instructions: Adhere to guidelines regarding food and drink consumption before the scan.
CT Scans in the Context of Sports Medicine
In addition to lung cancer diagnostics, CT scans have applications in sports medicine. Athletes may undergo CT scans to detect injuries in thoracic regions that can affect performance. Such use underscores the versatility and importance of CT technology in various medical fields.
The Future of CT Scans in Lung Cancer Diagnosis
As technology advances, the role of CT scans in lung cancer diagnosis will continue to evolve. Key developments include:
- Artificial Intelligence: AI algorithms are being developed to enhance image interpretation and detect anomalies more efficiently.
- Lower Radiation Doses: Innovations aim at reducing radiation exposure during CT procedures.
- Enhanced Imaging Techniques: Advanced CT modalities promise even better clarity and detail in imaging.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the CT scan for lung cancer is an indispensable tool in the arsenal of modern medicine. Its ability to provide detailed internal images plays a pivotal role in early detection and management of lung cancer, thereby improving patient outcomes significantly. As we look to the future, ongoing technological advancements promise to further enhance the efficacy and safety of this crucial diagnostic method.
The importance of spreading awareness about lung cancer and the vital role of CT scans cannot be overstated. By understanding these processes and advancements, both medical professionals and patients alike can take proactive steps towards better health, informed decisions, and potentially life-saving interventions.



